Sử dụng thông tin sau cho Câu 5 và Câu 6: Để đo thể tích máu của bệnh nhân, người ta tiêm vào máu của bệnh nhân một lượng dung dịch chứa đồng vị phóng xạ  có chu kì bán rã 27,7 ngày. Thể tích của dung dịch là không đáng kể so với thể tích máu của người. Độ phóng xạ của dung dịch tiêm vào bằng 5 mCi Sau khi tiêm 72 giờ, lấy ra 10 ml máu của người bệnh và đo độ phóng xạ thì thu được kết quả là 0,01 mCi.
có chu kì bán rã 27,7 ngày. Thể tích của dung dịch là không đáng kể so với thể tích máu của người. Độ phóng xạ của dung dịch tiêm vào bằng 5 mCi Sau khi tiêm 72 giờ, lấy ra 10 ml máu của người bệnh và đo độ phóng xạ thì thu được kết quả là 0,01 mCi.
Câu 5. Số nguyên tử trong dung dịch ban đầu là 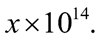 Giá trị của x là bao nhiêu? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần chục.
Giá trị của x là bao nhiêu? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần chục.
Câu 6. Thể tích máu của người bệnh đo được từ phương pháp này là bao nhiêu lít? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần chục.
ĐỀ VIP 4 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Sử dụng thông tin sau cho Câu 3 và Câu 4: Một người pha 200 ml nước ở 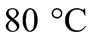 với 300 ml nước ở
với 300 ml nước ở 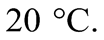 Cho khối lượng riêng của nước là 1000 kg/m3 và nhiệt dung riêng của nước là 4180 J/(kg.K). Sau khi đạt trạng thái cân bằng nhiệt, nhiệt độ của hệ là
Cho khối lượng riêng của nước là 1000 kg/m3 và nhiệt dung riêng của nước là 4180 J/(kg.K). Sau khi đạt trạng thái cân bằng nhiệt, nhiệt độ của hệ là
Câu 3. Nhiệt lượng do phân nước có nhiệt độ thấp hơn nhận vào trong quá trình trao đổi nhiệt là bao nhiêu kJ? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần chục.
Câu 4. Nhiệt lượng bị thất thoát ra ngoài trong quá trình trao đổi nhiệt giữa hai lượng nước cho tới khi cân bằng nhiệt là bao nhiêu kJ? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần chục.
ĐỀ VIP 4 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Sử dụng thông tin sau cho Câu 1 và Câu 2: Đặt một điện áp xoay chiều có tần số 50 Hz vào hai đầu một điện trở R. Đặt một Vôn kế vào hai đầu điện trở và một Ampe kế nối tiếp với điện trở. Số chỉ của hai thiết bị là 1,03 mA và 120,05 V.
Câu 1. Giá trị của điện trở là 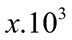 Giá trị của là bao nhiêu? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng đơn vị.
Giá trị của là bao nhiêu? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng đơn vị.
Câu 2. Xung quanh đoạn mạch này có điện từ trường lan truyền dưới dạng sóng điện từ. Chu kì của sóng điện từ này là bao nhiêu giây? Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần trăm.
Sử dụng thông tin sau cho Câu 3 và Câu 4: Một người pha 200 ml nước ở với 300 ml nước ở 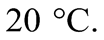 Cho khối lượng riêng của nước là 1000 kg/m3 và nhiệt dung riêng của nước là 4180 J/(kg.K). Sau khi đạt trạng thái cân bằng nhiệt, nhiệt độ của hệ là
Cho khối lượng riêng của nước là 1000 kg/m3 và nhiệt dung riêng của nước là 4180 J/(kg.K). Sau khi đạt trạng thái cân bằng nhiệt, nhiệt độ của hệ là 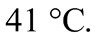
ĐỀ VIP 4 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 3. Hình vẽ bên là một mô hình của một động cơ điện một chiều. Trong hình bên có một nguồn điện có suất điện động không đổi 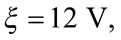 không có điện trở trong. Khung dây phẳng, cứng, hình chữ nhật ABCD có tổng điện trở của khung là
không có điện trở trong. Khung dây phẳng, cứng, hình chữ nhật ABCD có tổng điện trở của khung là 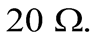 Xem từ trường là đều với cảm ứng từ cho biết ban đầu các đường sức từ song song với cạnh AB. Bộ phận X là một phần cứng, gắn liền với khung dây, có dạng hai vành tròn cách nhau bằng một khe nhỏ. Bộ phận Y là phần cứng gắn liền với nguồn điện, tiếp xúc và có thể trượt lên bề mặt của bộ phận X. Cả hai bộ phận X và Y đều dẫn điện. Bỏ qua suất điện động cảm ứng khi khung dây quay trong từ trường.
Xem từ trường là đều với cảm ứng từ cho biết ban đầu các đường sức từ song song với cạnh AB. Bộ phận X là một phần cứng, gắn liền với khung dây, có dạng hai vành tròn cách nhau bằng một khe nhỏ. Bộ phận Y là phần cứng gắn liền với nguồn điện, tiếp xúc và có thể trượt lên bề mặt của bộ phận X. Cả hai bộ phận X và Y đều dẫn điện. Bỏ qua suất điện động cảm ứng khi khung dây quay trong từ trường.
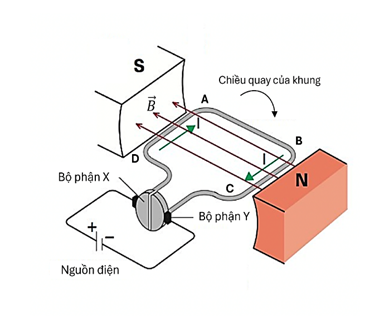
a) Cường độ dòng điện chạy trong khung dây là 60 mA.
b) Chiều quay của khung trong hình là không đúng.
c) Nhờ có bộ phận X và bộ phận Y, khung dây có thể quay mà không kéo theo nguồn điện.
d) Khi dòng điện không đổi được duy trì ổn định, khung dây quay với chiều không đổi.
Câu 4. Một chất chứa là một chất phóng xạ có chu kì bán rã 5,27 năm, được sử dụng như một phương pháp điều trị ung thư. Mẫu chất được xem là hết hạn sử dụng khi độ phóng xạ chỉ còn 70%.
a) Số hạt nhân của đồng vị trên trong mẫu chất giảm đều theo thời gian.
b) Hoạt độ phóng xạ của mẫu giảm đi 0,00025% sau mỗi phút.
c) Nếu mẫu được sản xuất vào tuần đầu tiên của tháng 8 năm 2024 thì vào tháng 6 năm 2026 mẫu này sẽ hết hạn sử dụng.
d) Giả sử có hai mẫu như trên được sản xuất cùng lúc. Sau một thời gian, hoạt độ phóng xạ của mỗi mẫu còn 50%. Khi đó, gộp hai mẫu này lại thành một thì độ phóng xạ có giá trị bằng với một mẫu vừa sản xuất.
ĐỀ VIP 4 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 1. Rót lượng nước có khối lượng ở nhiệt độ 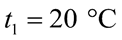 vào một nhiệt lượng kế. Thả trong nước một cục nước đá có khối lượng
vào một nhiệt lượng kế. Thả trong nước một cục nước đá có khối lượng 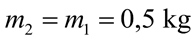 và nhiệt độ Cho nhiệt dung riêng của nước của nước đá
và nhiệt độ Cho nhiệt dung riêng của nước của nước đá 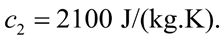 Nhiệt nóng chảy của nước đá Bỏ qua khối lượng của nhiệt lượng kế.
Nhiệt nóng chảy của nước đá Bỏ qua khối lượng của nhiệt lượng kế.
a) Nhiệt lượng nước đá nhận vào để tăng nhiệt độ lên đến là 15 kJ.
b) Để toàn bộ cục nước đá tan từ khi đạt cần nhận nhiệt lượng 180 kJ.
c) Nhiệt lượng nước tỏa ra để giảm nhiệt độ tới là 42 kJ.
d) Sau khi cân bằng nhiệt, nước đá tan hoàn toàn và nhiệt độ của hệ là 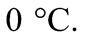
Câu 2. Cho một hỗn hợp khí trong xi lanh gồm 23 g Oxygen có khối lượng mol 32 g/mol và 87 g Nitrogen có khối lượng mol 28 g/mol.
a) Khối lượng mol của hỗn hợp là 28,95 g/mol.
b) Thể tích của xi lanh khi áp suất của hỗn hợp là 105 Pa, nhiệt độ là 86,5 lít.
c) Khối lượng riêng của hỗn hợp ở điều kiện câu b) là khoảng 1,15 g/lít.
d) Áp suất riêng phần của các phân tử Oxygen là khoảng 18,8 kPa.
ĐỀ VIP 4 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026