Sử dụng các thông tin sau cho câu 5 và câu 6: Tàu vũ trụ Voyager 1 (được phóng năm 1977) sử dụng nguồn năng lượng là hệ thống 3 máy phát nhiệt điện đồng vị phóng xạ (RTG). Nhiên liệu chính được sử dụng là Plutonium (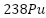 ), một chất phóng xạ á có chu kì bán rã là T = 87,7 năm. Khi phân rã, nhiệt lượng tỏa ra được các cặp nhiệt điện chuyển hóa thành điện năng. Biết rằng công suất phát điện của hệ thống tỉ lệ thuận với hoạt độ phóng xạ của nguồn nhiên liệu. Tại thời điểm phóng, tổng khối lượng
), một chất phóng xạ á có chu kì bán rã là T = 87,7 năm. Khi phân rã, nhiệt lượng tỏa ra được các cặp nhiệt điện chuyển hóa thành điện năng. Biết rằng công suất phát điện của hệ thống tỉ lệ thuận với hoạt độ phóng xạ của nguồn nhiên liệu. Tại thời điểm phóng, tổng khối lượng 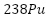 trong các máy phát là 13,5 kg và công suất phát điện của tàu là 470 W. Lấy 1 năm có 365 ngày và xem khối lượng mol nguyên tử bằng số khối hạt nhân.
trong các máy phát là 13,5 kg và công suất phát điện của tàu là 470 W. Lấy 1 năm có 365 ngày và xem khối lượng mol nguyên tử bằng số khối hạt nhân.
Câu 5: Độ phóng xạ ban đầu của lượng nhiên liệu hạt nhân trên tàu Voyager 1 là x.1015 Bq. Tìm giá trị của x. (Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần trăm)
Câu 6: Để các thiết bị khoa học quan trọng và hệ thống liên lạc trên tàu hoạt động, công suất điện tối thiểu cần duy trì là 200 W. Kể từ thời điểm phóng, tàu Voyager 1 có thể duy trì hoạt động tối thiểu trong bao nhiêu năm? (Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng đơn vị)
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Sử dụng các thông tin sau cho câu 3 và câu 4: Một cylinder hình trụ có chiều dài 51 cm, tiết diện trong 25 cm2, đặt thẳng đứng. Trong cylinder có một piston cách nhiệt mỏng có khối lượng 1 kg. Piston chia cylinder thành hai phần như hình, mỗi phần chứa lượng khí giống nhau. Khi nhiệt độ của khí trong hai phần cylinder cùng bằng 27oC thì đáy piston cách đáy cylinder 25 cm. Lấy g = 10 m/s2. Xem ma sát giữa piston và thành cylinder không đáng kể, nhiệt độ khí phần trên trong cylinder không đổi và giả định các khối khí đang xét là khí lí tưởng.
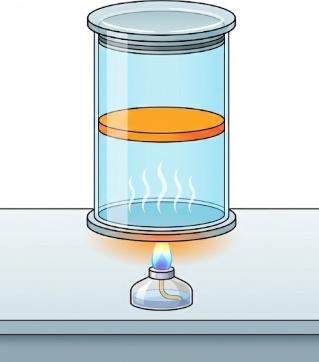
Câu 3: Áp suất của lượng khí ở phần trên trong cylinder tại trạng thái ban đầu bằng bao nhiêu kPa?
Câu 4: Để piston dịch chuyển đến vị trí chính giữa của cylinder thì cần nung nóng khí ở phần dưới cylinder đến nhiệt độ là bao nhiêu Kelvin? (Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng đơn vị)
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Sử dụng các thông tin sau cho câu 1 và câu 2: Một học sinh dùng một bếp điện có ghi (220V – 1000W) hoạt động ở đúng hiệu điện thế định mức để đun sôi 1,2 kg nước trong một chiếc ấm bằng nhôm có khối lượng 300g. Nhiệt dung riêng của nhôm và nước lần lượt là 880 J/kg.K và 4200 J/kg.K. Nhiệt độ ban đầu của nước và ấm là 20oC. Do nhiệt lượng bị thất thoát ra môi trường xung quanh, nhiệt lượng do bếp cung cấp không được chuyển hóa hoàn toàn để làm nóng nước. Học sinh quan sát thấy nếu ngắt điện thì cứ sau 1 phút, nhiệt độ của nước và ấm hạ xuống 1oC. Coi công suất tỏa nhiệt ra môi trường là không đổi trong suốt quá trình đun.
Câu 1: Công suất tỏa nhiệt trung bình ra môi trường xung quanh của nước và ấm bằng bao nhiêu W? (Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng phần mười)
Câu 2: Thời gian cần thiết để đun sôi lượng nước nói trên là bao nhiêu giây? (Làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số hàng đơn vị)
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 3. Hệ thống phanh tái sinh (Regenerative Braking) là công nghệ tiêu chuẩn trên các phương tiện giao thông chạy điện. Để đơn giản, ta xét mô hình động cơ điện một chiều trong xe có cấu tạo gồm: Stator là nam châm đứng yên tạo ra từ trường và Rotor là khung dây dẫn điện có thể quay quanh trục, được nối với bánh xe. Nguyên lí hoạt động của hệ thống dựa trên sự chuyển đổi chế độ làm việc của động cơ qua hai giai đoạn:
Giai đoạn xe di chuyển: Pin cấp điện vào khung dây. Dòng điện chạy trong khung dây được đặt trong vùng từ trường của nam châm và chịu tác dụng của lực từ làm khung dây quay, dẫn động bánh xe.
Giai đoạn xe giảm tốc: Nguồn điện cấp cho khung dây bị ngắt. Theo quán tính, bánh xe tiếp tục quay kéo theo khung dây quay trong từ trường của nam châm. Lúc này, động cơ chuyển sang chế độ máy phát điện, biến cơ năng thành điện năng để nạp lại cho pin.
a) Trong giai đoạn xe di chuyển, lực từ tác dụng lên các cạnh của khung dây tạo ra một ngẫu lực làm quay bánh xe.
b) Trong giai đoạn xe giảm tốc, từ thông qua diện tích khung dây biến thiên là nguyên nhân sinh ra dòng điện nạp cho pin.
c) Khi giảm tốc, dòng điện cảm ứng sinh ra trong khung dây tạo ra một ngẫu lực từ cùng chiều với chiều quay của bánh xe.
d) Nếu đang trong quá trình nạp điện, xe đang xuống dốc với tốc độ càng cao thì công suất điện thu hồi được càng lớn.
Câu 4. Dùng một proton () để bắn phá hạt nhân Lithium (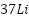 ) đứng yên để gây ra phản ứng:
) đứng yên để gây ra phản ứng:
Biết khối lượng của các hạt nhân: Cho khối lượng của neutron là 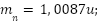 lấy 1u = 931,5 MeV/c2. Biết năng lượng liên kết riêng của hạt nhân X là 7,1 MeV/nucleon.
lấy 1u = 931,5 MeV/c2. Biết năng lượng liên kết riêng của hạt nhân X là 7,1 MeV/nucleon.
a) Hạt nhân X được tạo thành trong phản ứng là hạt nhân Helium ().
b) Độ hụt khối của hạt nhân bằng 0,0423u.
c) Phản ứng hạt nhân này tỏa ra năng lượng xấp xỉ 17,4 eV.
d) Hạt nhân bền vững hơn hạt nhân X.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 1. Trộn một khối nước đá có khối lượng 0,5 kg đang ở nhiệt độ –20oC vào một nhiệt lượng kế chứa 0,5 kg nước đang ở nhiệt độ 30oC. Bỏ qua nhiệt dung của nhiệt lượng kế và sự trao đổi nhiệt với môi trường. Cho nhiệt dung riêng của nước đá và nước lần lượt là 2100 J/kg.K và 4200 J/kg.K; nhiệt nóng chảy riêng của nước đá là ë = 3,34.105 J/kg.
a) Trong quá trình trao đổi nhiệt, khối nước đá thu nhiệt và khối nước tỏa nhiệt.
b) Nhiệt lượng cần thiết để chuyển khối nước đá từ –20oC lên 0oC là 21000 kJ.
c) Khi cân bằng nhiệt, lượng nước đá trong nhiệt lượng kế tan hết và hệ đạt nhiệt độ lớn hơn 0oC.
d) Tại trạng thái cân bằng, tổng khối lượng nước trong nhiệt lượng kế xấp xỉ bằng 626g.
Câu 2. Một mol khí lí tưởng thực hiện chu trình biến đổi được biểu diễn bằng đồ thị như hình vẽ bên dưới. Biết p1 = 8,31.105 Pa; T1 = 300 K; p2 = 13,85.105 Pa.
- Giai đoạn (1) sang (2): đồ thị là một phần của nhánh Parabol có đỉnh tại gốc tọa độ O (phương trình Parabol này có dạng T = aV2 với a là hằng số tính theo đơn vị K/m6);
- Giai đoạn (2) sang (3): Đồ thị là một đoạn thẳng có đường kéo dài vuông góc với trục OV;
- Giai đoạn (3) về (1): Đồ thị là một đoạn thẳng kéo dài đi qua gốc tọa độ O.
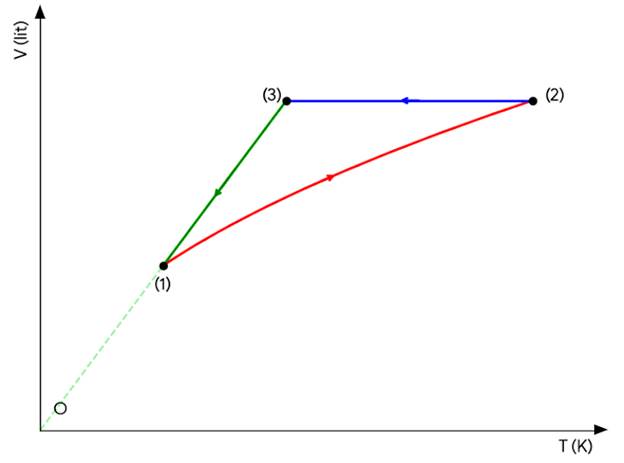

a) Đường 2 – 3 biểu diễn quá trình đẳng nhiệt.
b) Đường 3 – 1 biểu diễn quá trình đẳng áp.
c) Giá trị của a là 108.
d) Nhiệt độ T2 xấp xỉ bằng 833,3 K.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 17: Một khối khí lí tưởng có khối lượng 10,5g, chứa trong bình dung tích 3 lít có áp suất 300 kPa và nhiệt độ 18oC . Khối lượng mol của khí này gần nhất với giá trị nào sau đây?
A. 32 g/mol. B. 44 g/mol. C. 2 g/mol. D. 28 g/mol.
Câu 18. Hai bình kín A và B chứa cùng một loại khí có mật độ phân tử khí tương ứng là µ1 và µ2 = 0,5µ1. Nếu nhiệt độ tuyệt đối của bình B gấp 4 lần bình A thì áp suất của bình A và B lúc đó lần lượt là p1 và p2. Kết luận nào sau đây đúng?
A. p1 = p2. B. p1 = 0,5p2. C. p1 = 2p2. D. p1 = 4p2.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 15: Một đoạn dây dẫn thẳng mang dòng điện được đặt trong vùng từ trường đều sao cho phương của đoạn dây vuông góc với các đường sức từ. Khi đó, lực từ tác dụng lên đoạn dây dẫn có phương
A. vuông góc với đoạn dây dẫn và vuông góc với đường sức từ.
B. vuông góc với đoạn dây dẫn và song song với đường sức từ.
C. dọc theo dây dẫn và song song với đường sức từ.
D. dọc theo dây dẫn và vuông góc với đường sức từ.
Câu 16: Một chất phóng xạ X có hằng số phóng xạ là ë. Ban đầu tại thời điểm t = 0s, một mẫu có N0 hạt nhân X. Tại thời điểm t, số hạt nhân X đã bị phân rã là
A. ΔN = N0.e–ët. B. ΔN = N0.(1 – e–ët).
C. ΔN = N0.(1 – eët). D. ΔN = N0.eët.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 13: Một vòng dây được đặt trong từ trường có từ thông vòng dây biến thiên trong khoảng thời gian . Biểu thức tính suất điện động cảm ứng trong vòng dây là
A. 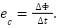 B. C.
B. C. 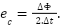 D.
D.
Câu 14: Điện áp xoay chiều (đơn vị của thời gian t là s) có tần số là
A. 50 Hz. B. 100 Hz. C. 100ð Hz. D. 50ð Hz.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 11: Theo mô hình động học phân tử, ở thể lỏng, các phân tử
A. dao động quanh vị trí cân bằng cố định. B. chuyển động hỗn loạn.
C. dao động quanh vị trí cân bằng không cố định. D. đứng yên.
Câu 12: Trong hệ tọa độ (p, T), đường đẳng tích là
A. đường thẳng song song với trục Op. B. đường thẳng song song với trục OT.
C. đường hyperbol. D. đường thẳng nếu kéo dài thì đi qua gốc tọa độ.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026
Câu 9: Xét một khối khí lí tưởng xác định, định luật Charles cho biết hệ thức liên hệ giữa
A. áp suất và nhiệt độ tuyệt đối khi thể tích không đổi.
B. thể tích và nhiệt độ tuyệt đối khi áp suất không đổi.
C. thể tích và áp suất khi nhiệt độ không đổi.
D. thể tích, áp suất và nhiệt độ tuyệt đối của khí.
Câu 10: Một học sinh thực hiện thí nghiệm để xác định độ lớn lực từ giữa hai nam châm như hình vẽ: đặt nam châm 1 trên cân thì số chỉ của cân là 80,0g; sau đó đặt nam châm 2 phía trên nam châm 1 thì số chỉ của cân là 83,1g. Gia tốc trong trường tại nơi làm thí nghiệm là 9,8 m/s2. Thí nghiệm này cho biết
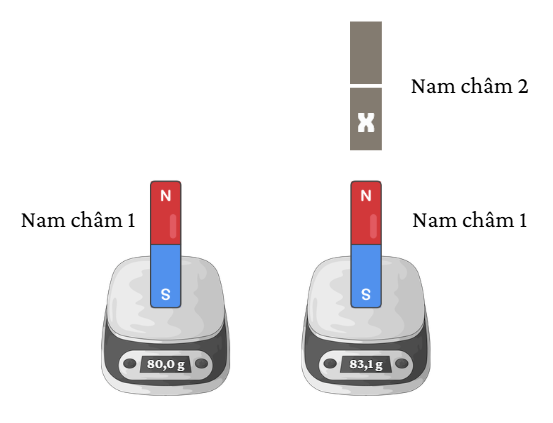
A. Độ lớn lực từ tương tác giữa nam châm là 30,38 mN.
B. Cực từ X của nam châm 2 là cực nam.
C. Khối lượng của nam châm 2 là 3,1 g.
D. Lực từ tương tác giữa hai nam châm là lực hút.
ĐỀ VIP 14 - KĐ - MỤC TIÊU 9+ TN THPT MÔN VẬT LÝ 2026